Electrolysis is the method by which hydrogen is produced using renewable resources. It’s the way in which hydrogen earns its ‘green‘ medal.
The process of electrolysis uses electricity to split water into hydrogen and oxygen, and this takes place in a unit called an electrolyzer.
Electrolyzers can vary in size, from large production plants attached directly to renewable electricity facilities (such as a wind farm), down to small units for smaller distribution requirements.
How does an electrolyzer work?
An Electrolyzer consists of a cathode and an anode separated by an electrolyte. Different types of electrolyte materials are used, meaning that electrolyzers don’t all work in precisely the same way, but the overall process is the same.
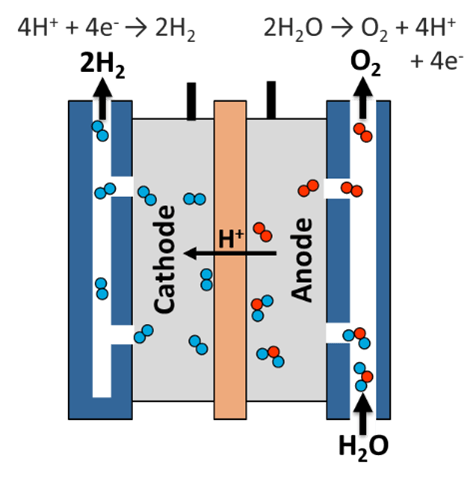
Diagram shows an electrolyzer. The process of electrolysis uses electricity to split water into hydrogen and oxygen, and this takes place in a unit called an electrolyzer.
If the source of electricity being used for electrolysis is renewable (ie wind, solar, hydro etc) then the Hydrogen it produces results in zero greenhouse gas emissions. This is how hydrogen as an energy source has earned its green credentials.
The majority of the electricity produced by the UK’s national grid is made using technology that creates greenhouse gas emissions. Therefore powering an electrolyzer using electricity from the grid is neither efficient or green.
So when looking at the benefits of hydrogen as an energy provider, it’s important to consider where the energy has come from to make it, and how green that source is.
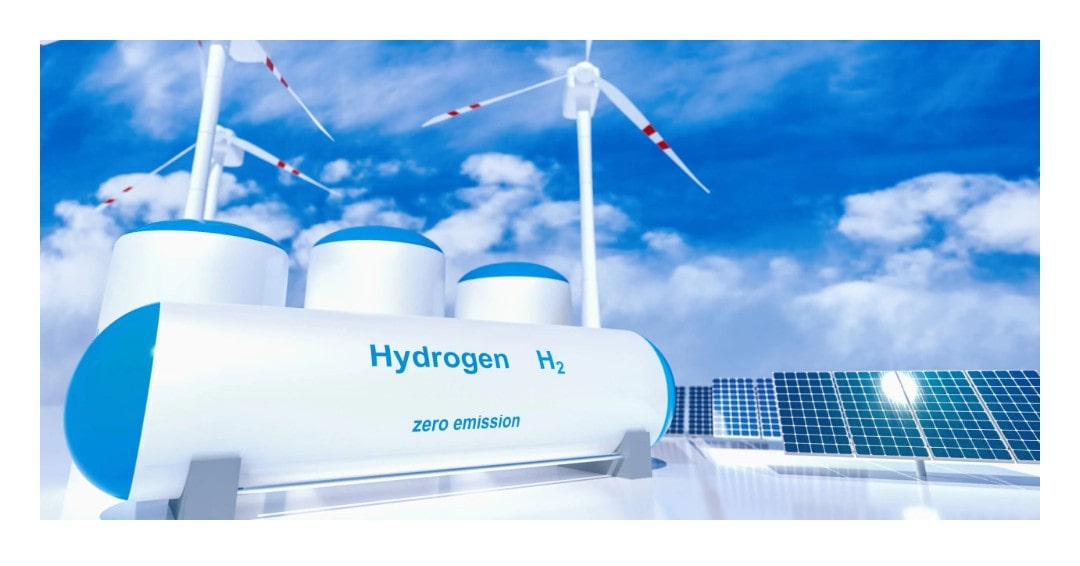

Renewable electricity powers the process of electrolysis in order to create renewable ‘green’ hydrogen, which can then be used to power transport systems, industrial plants and home heating, all with zero emissions.






